What are NbS?
Need a quick refresh on NbS? Click here!
Why support R&I on NbS?
This roadmap was developed in response to the growing need for collaborative processes among stakeholders at every stage of the Nature-based Solutions (NbS) process, including design, implementation, governance, and monitoring due to their multiple objectives, impacts, and potential for benefits. Research and innovation (R&I) can play a crucial role in exploring action levers and addressing barriers essential for the deployment of NbS and with NbS expected to support the implementation of the EU Green Deal, coordinated knowledge development and implementation are vital to support decision-making and unify European efforts toward common goals.
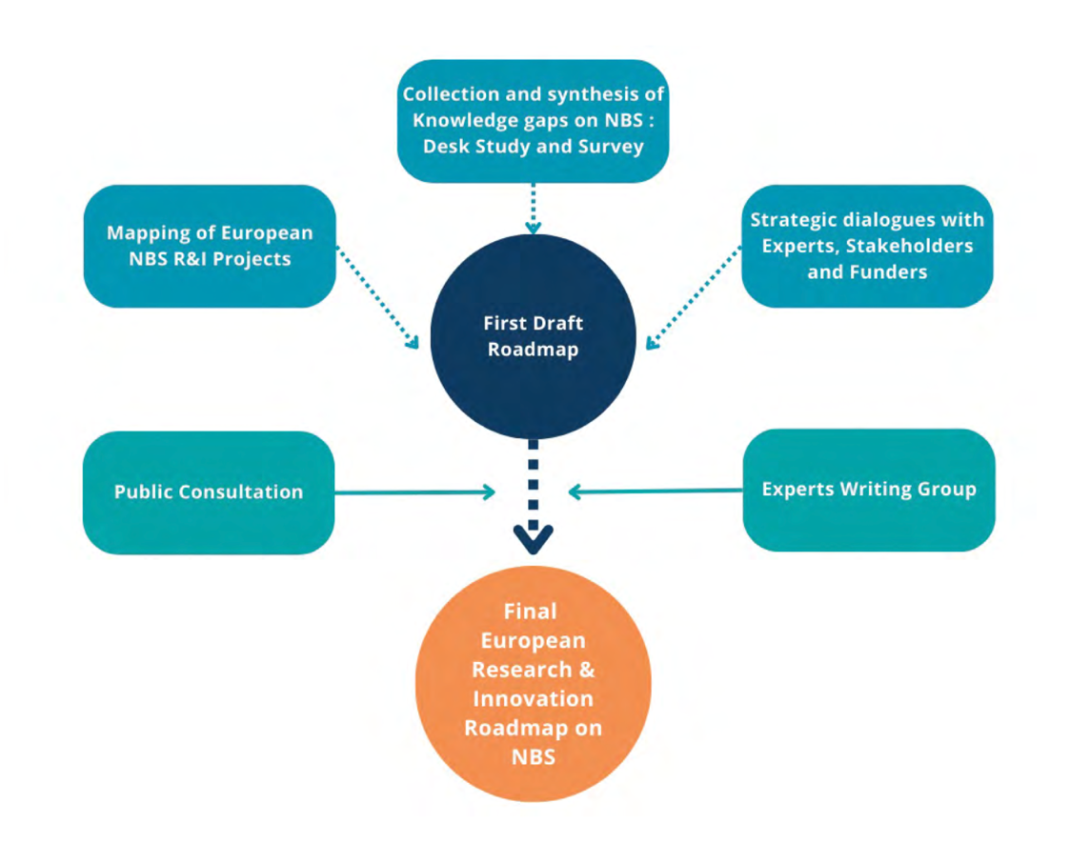
How as the R&I Roadmap designed?
This Roadmap was co-developed with a wide diversity of stakeholders. It draws on NetworkNature’s activities, including a mapping endeavor of European NbS R&I projects and an extensive collection of knowledge gaps identified from literature and stakeholder input.
Understanding the bigger picture: the socio-political context
NbS have come a long way since their emergence in the late 2000s, finding a wide diversity of applications, for instance in climate mitigation, urban resilience, disaster risk reduction (Cassin & Matthews 2021). Recently, their significance has grown, particularly in response to environmental-related challenges (Davies et al. 2021).
In Europe, this interest surge is mirrored in academic and political publications. Key EU policies, including the European Green Deal, the EU Biodiversity Strategy, the Climate Adaptation Strategy, and the European Commission (EC) Framework Programme for Research and Innovation (e.g., Horizon Europe) prominently feature NbS. Despite this, their integration into sectors beyond environmental and research policies remains limited.
Globally, major organisations such as the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), and the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) have incorporated NbS into their work plans and publications. This growing recognition is also evident in recent strategic documents, specifically the Sharm El-Sheikh Declaration from the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework from the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Furthermore, research highlights the growing role of “nature-based enterprises” in responding to the increasing demand for NbS, which is supported by the private sector’s growing interest in NbS. However, criticisms such as greenwashing, unequal distribution of benefits or lack of cost-effectiveness persist. These challenges represent strong barriers to NbS deployment, and addressing them requires robust evidence, capacity-building and engagement to harness NbS’s potential for tackling societal challenges while ensuring environmental, social and economic sustainability.
Cassin, J., Matthews, J. H., & Lopez-Gunn, E. Nature-based solutions and water security: An action agenda for the 21st Century. Elsevier Science. (2021).
Davies, C., Chen, W. Y., Sanesi, G. & Lafortezza, R. The European Union roadmap for implementing nature-based solutions: A review. Environ. Sci. Policy 121, 49–67 (2021).